IACS Organizational Structure
The International Association of Classification Societies, more commonly known as the IACS, was founded in 1968 by seven leading classification societies (ABS, BV, DNV, GL, LR, NK, RINA) in order to promote the improvement of standards for ensuring safety at sea and the prevention of pollution of the marine environment, promote communication and cooperation with relevant international and national maritime organizations, and allow for enhanced cooperation with the global maritime industry. Including ClassNK, IACS currently has a total of 12 member societies, and at present more than 90% of the world’s international commercial fleet (gross tonnage base) is registered under IACS member societies.
The IACS organizational structure is as shown below.
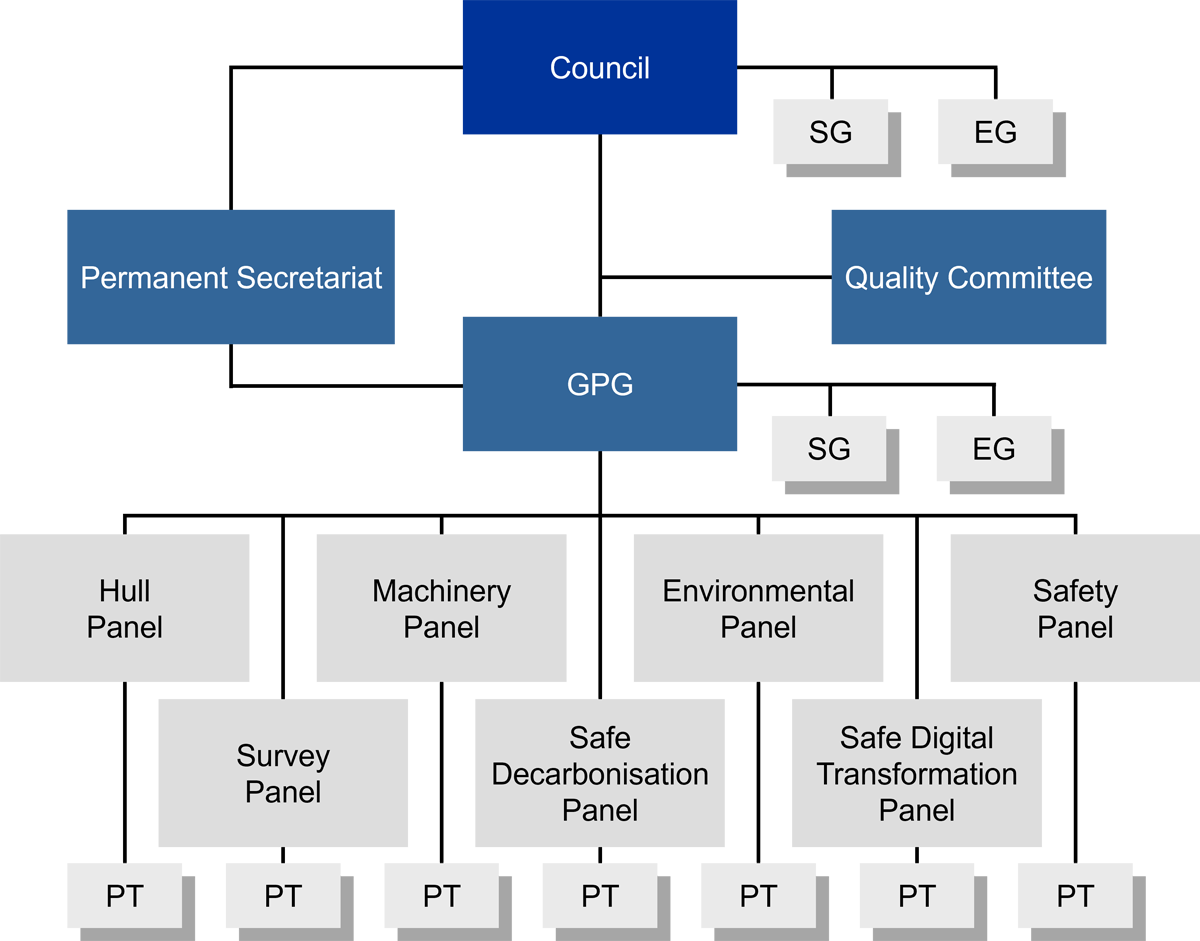
IACS Organizational Structure
★GPG: General Policy Group, SG: Small Group, EG: Expert Group, PT: Project Team
The IACS consists of the Council, which is the governing body of the Association, and the General Policy Group (GPG), which handles general policy matters. The IACS Permanent Secretariat, which has been located in London since 1992, handles secretarial operations such as communications with the IMO, assisting the Council/GPG Chairpersons, and other activities. IACS also maintains a Quality Committee to manage the IACS quality system, Small Groups (SG) comprised of a small number of members created to investigate and carry out specific tasks and report to Council or GPG, as well as Expert Groups (EG) comprised of experts from each of the member societies.
Under GPG, there are seven (7) Panels (Hull, Machinery, Survey, Environmental, Safe Decarbonisation, Safe Digital Transformation and Safety), which are mainly in charge of technical matters associated with the development and revision of Unified Requirements (UR) and Unified Interpretations (UI). Further, Project Teams (PTs) comprised of a small number of members have been set up under each Panel to efficiently address specific technical matters within a certain period.
Council
The main role of the IACS Council is to make public the essential role that the IACS plays in maintaining standards for ship safety and protection of the marine environment. The Council is also tasked with promoting the role of classification and the high quality of IACS members to the greater maritime industry, as well as executive decision-making related to the association, including establishing appropriate measures towards member societies which fall below the Association’s high standards. As the ultimate decision-making body within IACS, the Council additionally makes important organizational decisions including the appointment of the Secretary General and the GPG Chairperson, as well as the final approval of IACS’ budget and related financial concerns.
General Policy Group (GPG)
The role of the GPG is to develop and implement the policies, strategies and long-term plans of the Council, to periodically review and revise the scope of work and mandate of each of the Panels, to oversee and approve each Panel’s work programme and budget, and to review and formally adopt the technical resolutions developed by the Panels. GPG is further responsible for approving the establishment of joint industry working groups (JIWG) with industries on specific technical topics and reporting on the outcomes of the JIWG to the Council and the greater maritime industry. GPG is also tasked with monitoring and responding to those activities of the IMO and other organizations which relate to the operations of the IACS.
Panels
The role of the Panels is to develop and update relevant IACS Resolutions such as UR and UI, to monitor and participate in the work of relevant organizations (e.g. IMO, ILO etc.) relating to the Panel’s field of expertise, and to identify important issues related to the Panels’ activities and propose relevant actions to be taken by the IACS to GPG. At present, the IACS consists of seven (7) Panels specialized in the fields of Hull, Machinery, Survey, Environmental, Safe Decarbonisation, Safe Digital Transformation and Safety matters, respectively. A brief overview of each Panel’s field of expertise is shown below.
(1) Hull Panel
The Hull Panel addresses all technical items related to the structure of ships including Common Structural Rules (CSR) such as loads and strength, materials and welding and hull damages
(2) Machinery Panel
The Machinery Panel addresses all technical items related to the mechanical and electrical systems of ships, such as propulsion systems, auxiliary machinery systems, and electric power generation and distribution systems, as well as machinery damage.
(3) Survey Panel
The Survey Panel addresses all technical items related to the survey and certification of ships, components and materials.
(4) Environmental Panel
The Environmental Panel addresses all technical items related to international instruments, e.g. IMO and other bodies, on environmental issue, such as marine pollution, air pollution and energy use.
(5) Safe Decarbonisation Panel
The Safe Decarbonisation Panel addresses all technical items related to safety requirements for all aspects of delivery, loading, storage, handling and use of alternative energy source and fuels onboard ships, etc.
(6) Safe Digital Transformation Panel
The Safe Digital Transformation Panel addresses all technical items related to the digitalization including shipboard automated electronic systems, system integration, cyber resilience of ships, Marine Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS), data management and exchange within the maritime sector, and advanced digital technologies in ship design appraisals and survey regimes.
(7) Safety Panel
The Safety Panel addresses all technical items related to the maritime safety of ships, equipment and personnel.