Topics at IMO
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is a specialized international agency of the United Nations. The IMO’s primary purpose is to ensure cooperation between Administrations with regards to all manners of technical instruments and conventions affecting international maritime trade, and to promote the safety of shipping, effective maritime operations, and the prevention of marine pollution by ships.
IMO, whose membership includes some 170 Member States and 110 participating NGOs, works constantly to establish, update and revised safety criteria for ship construction and equipment, technical requirements and limits for cargo loading, prevention of oil pollution, and emission of harmful substances and exhaust gas from the ships, environmental protection, maritime security, among other areas.
An overview of the IMO structure can be seen in the chart below. IMO is governed by the IMO Assembly and the IMO Council. Beneath the Council, there are five main Committees, including the Maritime Safety Committee, which addresses issues related to safety at sea, and the Marine Environment Protection Committee which addresses issues related to protection of the environment. In order to ensure effective operations, numerous sub-committees have been established which report to their parent committees and provide advice on technical matters.
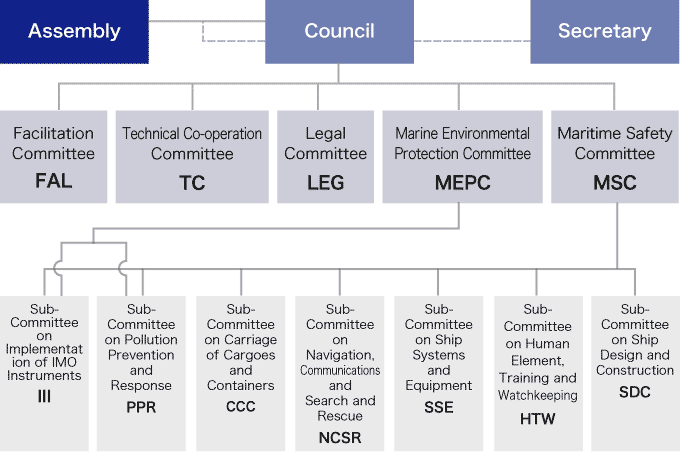
IMO Structure
Assembly
The Assembly is the governing body of the IMO and consists of all of the member states and meets every two years. The Assembly determines the IMO’s work plan and budget, as well as carrying our elections of new members and other organizational tasks.
Council
The IMO council consists of 40 Member States which serve a term of 2 years on the Council.
MSC (Maritime Safety Committee)
The MSC is composed of all the IMO Member States and meets three times over a two year span.
MSC is tasked with “considering any matter within the scope of the Organization concerned with aid to navigation, construction and equipment of vessels, manning from a safety standpoint, rules for the prevention of collisions, handling of dangerous cargoes, maritime safety procedures and requirements, hydrographic information, log-books and navigational records, marine casualty investigations, salvage and rescue and any other matters directly affecting maritime safety”. Further information about the activities of MSC and its Sub-Committees are available at the link below.
MEPC (Marine Environment Protection Committee)
MEPC is composed of all the IMO Member States and meets three times over a two year span. MEPC is tasked with “considering the prevention and the control of pollution from ships and related rules.” Further information about the activities of MEPC and its Sub-Committees is available at the link below.
Sub-Committee
Sub-Committees consist of all the IMO Member States and meet annually.
Each Sub-Committee carries out specialized discussions of on specific technical matters and then reports their findings to their parent committees (i.e. MSC and MEPC) for further action, for example the revision of conventions and other instruments.
Outcome of the IMO discussion and the ratification status of the convention
Outcomes of MSC and MEPC meetings are available at the link below.
- Preliminary Report of IMO MEPC Extraordinaty Session (October 2025)
- Preliminary Report of IMO MEPC Extraordinaty Session (October 2025) – Korean Version
- Outcome of MSC110 (June 2025)
- Outcome of MEPC83 (April 2025)
- Outcome of MSC109 (December 2024)
- Outcome of MEPC82 (October 2024)
- Outcome of MSC108 (May 2024)
- Outcome of MEPC81 (March 2024)
- Outcome of MEPC80 (July 2023)
- Outcome of MSC107 (June 2023)
- Outcome of MEPC79 (December 2022)
- Outcome of MSC106 (November 2022)
- Outcome of MEPC78 (June 2022)
- Outcome of MSC105 (April 2022)
- Outcome of MEPC77 (November 2021)
- Outcome of MSC104 (October 2021)
- Outcome of MEPC76 (June 2021)
- Outcome of MSC103 (May 2021)
- Outcome of MSC102 (November 2020)
- Outcome of MEPC75 (November 2020)
- Outcome of MSC101 (June 2019)
- Outcome of MEPC74 (May 2019)
- Outcome of MSC100 (December 2018)
- Outcome of MEPC73 (October 2018)
- Outcome of MSC99 (May 2018)
- Outcome of MEPC72 (April 2018)
- Outcome of MEPC71 (July 2017)
- Outcome of MSC98 (June 2017)
- Outcome of MSC97 (November 2016)
- Outcome of MEPC70 (October 2016)
- Outcome of MSC96 (May 2016)
- Outcome of MEPC69 (April 2016)
- Outcome of MSC95 (June 2015)
- Outcome of MEPC68 (May 2015)
- Outcome of MSC94 (November 2014)
- Outcome of MEPC67 (October 2014)
- Outcome of MSC93 (May 2014)
- Outcome of MEPC66 (April 2014)
- Outcome of MSC92 (June 2013)
- Outcome of MEPC65 (May 2013)
- Outcome of MSC91 (November 2012)
- Outcome of MEPC64 (October 2012)
- Outcome of MSC90 (May 2012)
- Outcome of MEPC63 (March 2012)
- Outcome of MEPC62 (July 2011)
- Outcome of MSC89 (May 2011)